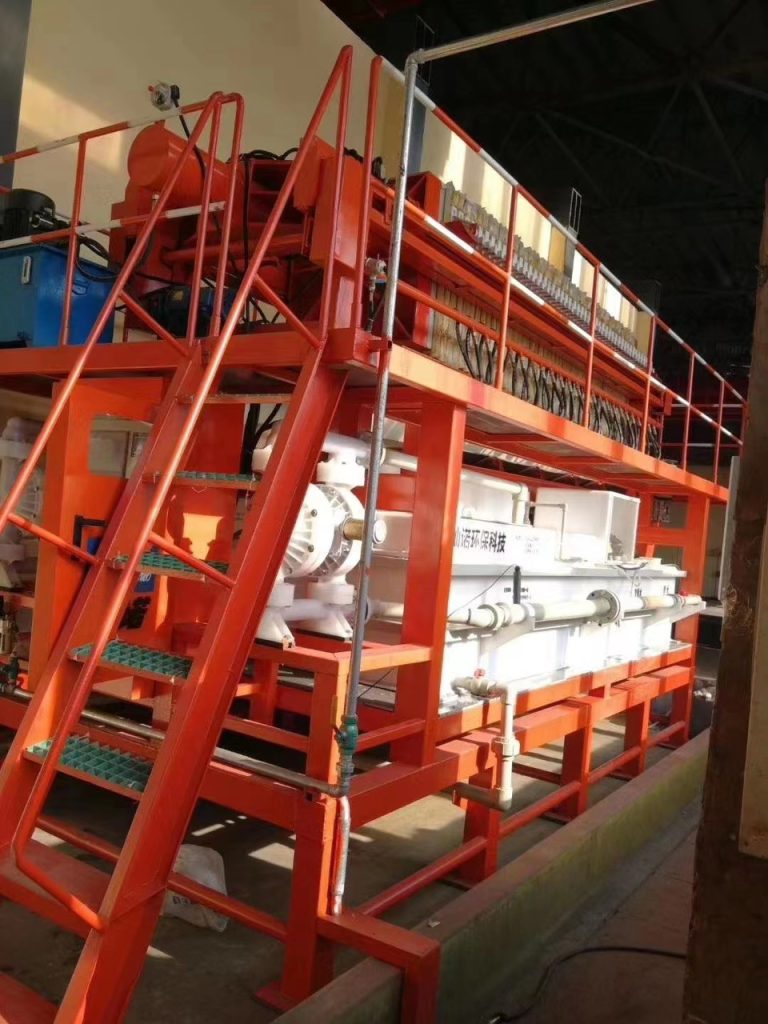
Automatic Iron Removal System (FCS) Features:
1. Applying the pipeline reaction treatment method and making full use of ammonia and hydrogen peroxide to reduce pollution and harm to humans;
2. Accurately measure pH and automatically add medicine, minimizing the influence of human factors on manual operation;
3. Complete, accurate and appropriate dosage calculation method of corresponding chemicals, which can remove iron without affecting the plating flow;
4. The automatic probe cleaning function greatly improves the accuracy and life of the probe, while reducing manual workload;
5. Automatic dual pump circuit technology allows the device to remove iron 24 hours a day without stopping;
6. Multi-sludge warning reminder, water level warning reminder, ammonia reminder, hydrogen peroxide reminder and other function reminders;
7. Remote monitoring alarm reminder function (optional);
8. Steel materials such as filter presses, frames, and railings must be treated with zinc-rich paint to prevent corrosion;
9. Filter press chamber drying function;
10. Pneumatic diaphragm pumps replace centrifugal pumps, which greatly improves the water supply efficiency and maintainability of the equipment (simplifies maintenance);
11. When choosing mechanical and electrical materials, consider a margin of 2-3 times the national standard;
12. The structural design of the mud discharge chute facilitates many operations
13. The company has a professional maintenance team responsible for pre-sales and after-sales service, product maintenance and support.
Effect of iron in liquid zinc solution on hot-dip galvanizing
The solubility of iron in zinc solution increases as the temperature increases. When the temperature is higher than 450°C, the solubility of iron in zinc solution is about 0.035%, when it exceeds 0.035% iron will react with zinc to form FeZn7 which has a density greater than the density of zinc solution and sinks The bottom of the pot is bottom slag. When the zinc solution contains aluminum, the excess iron in the zinc solution will react with aluminum to form Fe2Al5 with a lower density, which will float above the zinc solution and become a residue. According to the molecular formula, it can be seen that these two types of zinc slag, when formed, consume a large amount of iron, elemental zinc and aluminum. The presence of iron in the zinc liquid increases the viscosity and surface tension of the zinc liquid, reduces fluidity and worsens the wetting conditions of the zinc liquid on steel. In addition, the presence of iron in the zinc liquid will also increase the hardness of the coating and hinder recrystallization. In short, excess iron will be harmful, causing the coating to become brittle, the surface to darken, increasing the amount of zinc slag and also increasing the consumption of zinc and aluminum.
Comparison Table for Selecting PCS Equipment Systems
|
Specifications |
Appearance
Size |
Equipment Capacity | Air Consumption (m3/h) | Power Supply Requirements | Iron Removal Capacity | Automatic/Manual Filter Press Configuration Instructions | Membrane Pump Configuration (hours) | Automatic Dosing Device (ammonia and hydrogen peroxide) | Suitable Output (tons/day) |
Operation and Troubleshooting Instructions |
| FCS-15 | 3200*2000*2520 |
3.0 |
125 | 125 | AC380A/5 wires | 5-8 | 15 | 2.0
(Domestic) |
lower than 80 |
Yes |
| FCS-30 | 4200*2100*2520 |
4.0 |
140 | 140 | AC380A/5 wires | 15-20 | 30 | 1.5
(Imported) |
80-150 |
Yes |
| FCS-60 | 5200*2300*2700 |
4.0 |
240 | 240 | AC380A/5 wires | 30-40 | 60 | 2.0
(Imported) |
50-250 |
Yes |
| FCS-100 | 6200*2400*2800 |
5.5 |
468 | 468 | AC380A/5 wires | 60-80 | 100 | 3.0
(Imported) |
250-400 |
Yes |

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)


