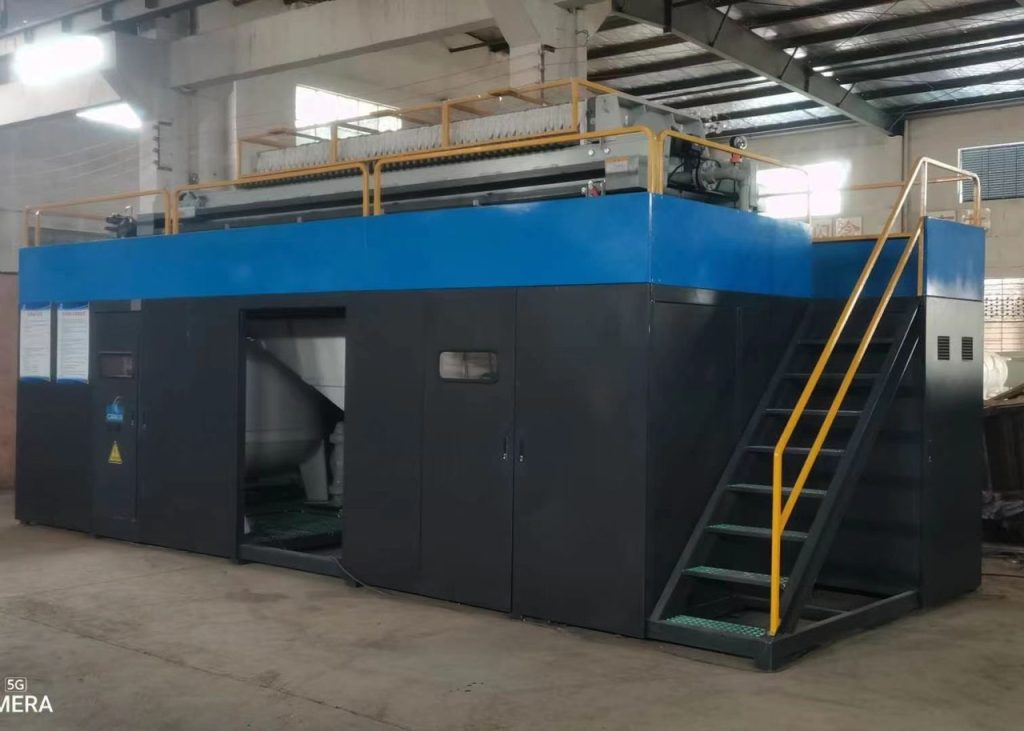
Background
In the industrial production of hot-dip galvanizing, steel after pickling with hydrochloric acid needs to be cleaned before being immersed in the zinc pot for hot plating. Impurities in the cleaning tank and flux tank mainly come from the acid tank.
Many manufacturing companies today have inconsistent methods of treating wash water and plating aids. In the process of treating wash water and plating aids, many companies now use sodium hydroxide or quicklime for neutralization treatment. , leading to the generation of a large amount of wastewater that needs to be treated. Chloride and COD exceeding the standards return to the production system causing large chloride accumulation, affecting normal production concentrations and wastewater treatment, and causing the treated water to not meet discharge standards. A large amount of impurities are continuously circulated in the production system or taken to the next stage, increasing the production and processing costs of the enterprise. To ensure the production process goes well, cleaning water and plating aid must be used to remove iron on the line to improve the situation.
Design principles
– Fully consider the principles of circular economy and strive to save operating costs.
– Regarding the selection of equipment and materials, it is necessary to choose appropriately based on the compositional characteristics of the cleaning solution and plating aid solution.
– Select equipment and pipes with outstanding features to seek harmony, unity, economy and applicability.
The role of cleaning water and iron removal methods
a. The role of cleaning water
– Remove residual hydrochloric acid on the surface of plated parts.
– Removes residual iron ions on the surface of plated parts.
– Degreasing, absorbing, suspending and dispersing dirt to prevent dirt from re-adhering to the surface of plated parts.
b. The main ingredient in cleaning water in the cleaning tank is H2O water, in addition to Fe2+, Zn2+, H+Cl- ions, defoaming agents, chelets, sludge, impurities and other metal ions.
c. Principle of iron removal reaction
HCl + NH4OH = H2O + NH4Cl
FeCl2 + 2NH4OH = 2NH4Cl + Fe(OH)2
FeCl3 + 3NH4OH = 3NH4Cl + Fe(OH)3
4Fe(OH)2 + O2 + 2H2O = 4Fe(OH)3
Fe(OH)2 + 2H2O2 = Fe(OH)3 + H2O + H+
d. Reliability of the filter membrane
Because the iron precipitate particles produced are much larger than the diameter of the membrane pores, the iron precipitates are retained in the purifier and the water is returned to the cleaning tank for recycling.
Analysis of iron removal by plating current
- Analysis of plating stream composition
In the plating aid reaction tank, the main ingredients are zinc chloride, ammonium chloride, explosion-proof agents, etc. In addition, there are iron chloride, H+ ions, OH- ions, sludge, impurities and ions. other metals,… zinc chloride, ammonium chloride and explosion-proof substances can exist stably in solvent environments with pH values from 0 ~ 4.5; Ferric chloride, sludge, impurities and other metal ions are the main sources of zinc slag and zinc dust formation.
- Principles of chemical reactions
HCl + NH4OH = H2O + NH4Cl
FeCl2 + 2NH4OH = 2NH4Cl + Fe(OH)2
FeCl3 + 3NH4OH = 3NH4Cl + Fe(OH)3
4Fe(OH)2 + O2 + 2H2O= 4Fe(OH)3
Fe(OH)2 + 2H2O2 = Fe(OH)3 + H2O +H+
- Precise control availability
The high-speed and stable data acquisition input and output control system (nTouch) has a signal sampling rate > 1Kbps and communication rate > 9600bps, so ammonia and hydrogen peroxide can be supplemented. in appropriate proportions.
- Reliability of the filter membrane
Because the iron precipitate particles produced are much larger than the diameter of the membrane pores, the zinc chloride will return to the ammonium chloride bath and the zinc chloride will return to the plating aid bath.
Feasibility of combined treatment for iron removal from cleaning water and iron removal from plating aid
- Analyze internal components
As can be seen above, the components contained in cleaning water (Fe2+, Zn2+, H+, Cl- ions, sludge, impurities, H2O and other metal ions,…) are all present in the plating aid, and the impurities in the cleaning water are also impurities of the plating aid.
- Analysis of iron removal methods
It can be seen from the principles of iron removal in cleaning water and iron removal in plating aid that the basic iron removal methods are the same.
Sơ đồ
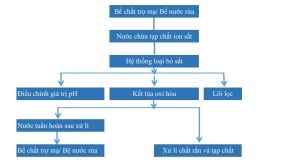
Attention:
– Water containing impurities in the plating tank/clear water tank is treated on the line with an “iron removal system”, the water is cleaned and discharged into the plating tank/clear water tank;
– Solid impurities, (mainly iron hydroxide) filtered out by the “iron removal system” are used as construction materials (made into high strength porous bricks and materials needed for cement factories )
– The equipment can select treatment capacity based on the amount of ferric chloride produced. Keep the iron chloride content in the plating tank below 1g/L.
Conclude
From the above comparison of impurity removal in cleaning water and iron removal in plating aid, the impurity components removed are basically the same, and the iron removal method is basically the same. alike. To ensure that the function of the plating aid is effective and that zero discharge can be achieved. Under the target conditions, the cleaning water should be completely abandoned and introduced directly into the plating aid to

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)


